How to browse this RBA model
An RBA model is defined in the form of XML files. An RBA model structure, model parameters, and simulation results can be exported as SBtab table files. SBtab files were used to generate these HTML pages.
The Main page gives an overview of the model. Each type of variables or constraints is described by a table. To get to the tables, you can click on the overview graphics on the main page or use the dropdown menus on top of each page. The original SBtab files for this model are available on the Main page.
RBA model structure
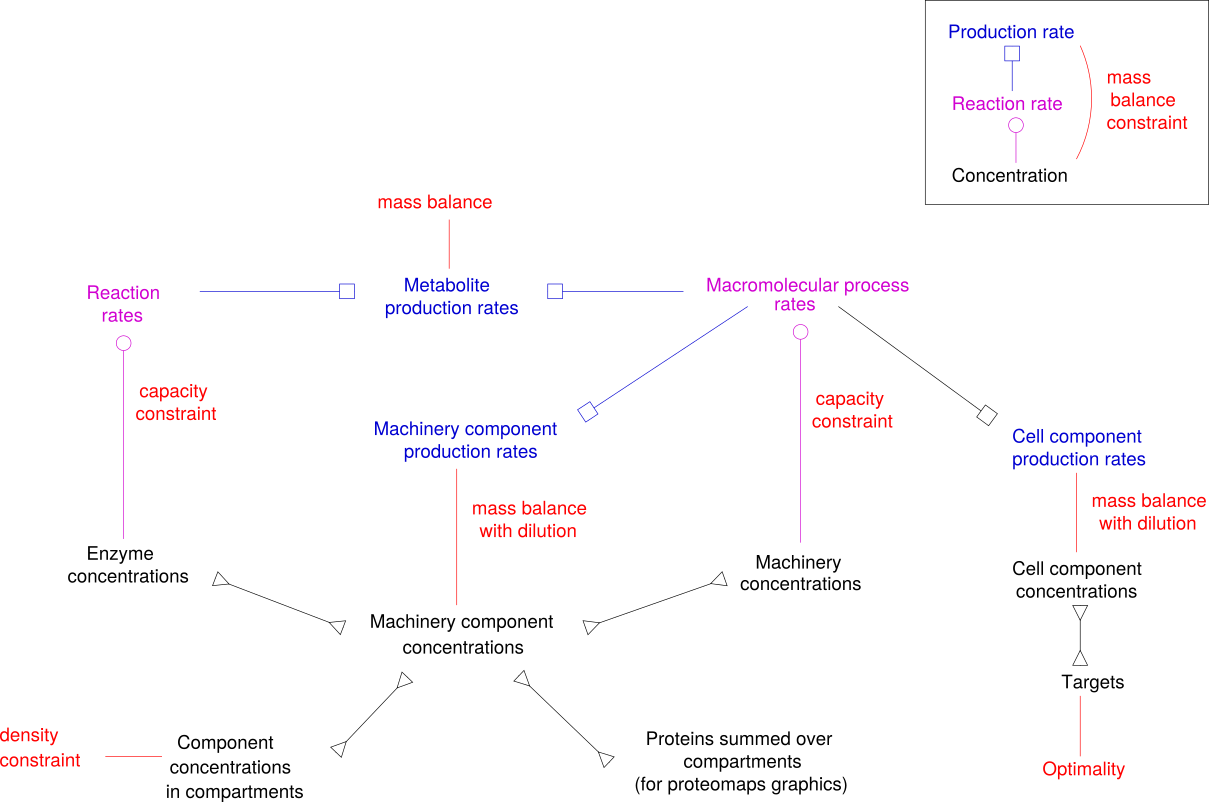
The graphics below summarises the variables and constraints in an RBA model. Items in the graphics correspond to model tables (except for "Mass balance with dilution" and "Optimality", which are not explicitly described by tables. The typical optimality criterion in RBA is growth rate maximisation. Metabolite concentrations (except for cellular targets) are also not described.
A table page provides the following functionality
- Sort table alphabetically To sort a table alphabetically (with respect to a column), click on the column header.
- Filter for search strings Enter a text string in the "Search" field to filter a table for rows containing this string.
- Hide columns Use the dropdown menu "Hide columns" to hide individual columns.
- Export .tsv file Use TSV button to export .tsv file showing the table (filtered by current search string)
- Export .pdf file Use PDF button to export .pdf file showing the table (filtered by current search string)
- Export .xlsx file Use XLS button to export .xlsx file showing the table (filtered by current search string)
- Links within model Some table elements provide links to elements in other tables. For example, links in the column "Enzyme" in table Reactions allow you to jump from a reaction to its catalysing enzyme.
- External links Links to external information. Some tables (e.g. Metabolites) may contain annotations that link an element to entries in other databases. Click on the links to get to these external web pages.
Tips and tricks
- View collapsed table cellsTo make tables better readable, large table cells have been collapsed (and replaced by "[Expand]"). To see their contents, hover over the cell with the mouse.
- Model statistics The table "Model size" (in the dropbdown menue "Model" on top) provides count numbers of various types of model elements.
- Empty tables If a table is empty, this means that the model does not contain the corresponding type of variable or constraint.
- Link to main page The model logo (next to the model name in the bar on top) bring you to the main page of this model. The RBA logo on the top left brings you to the RBA home page.
Remarks on specific table columns
- Metabolites !Type: "external": extracellular; "internal": intracellular, balanced within metabolism; "precursors": intracellular macromolecule precursors, balanced between metabolism and macromolecule production.
- Reactions !Type: "exchange": exchange reaction (between outside world and growth medium); "normal": normal (intracellular) reaction; "Transport": Transport between extracellular medium and cell.
Learn more about Resource Balance Analysis
For further information on RBA, please visit rba.inrae.fr.
Credits
Resource Balance Analysis (RBA) has been developed by Anne Goelzer, Vincent Fromion, Stéphane Fischer, and Oliver Bodeit at INRAE (French National Research Institute for Agriculture, Food and Environment). The HTML display has been developed by Inès Ben-Samir, Wolfram Liebermeister, and Oliver Bodeit.
Funding
